As we’ve been exploring in our most recent series, the OTT market’s shift to live streaming sports and other linear content calls for a new, comprehensive approach to battling piracy. Given the far-reaching complexities of these issues, just identifying what constitutes an effective approach is a challenge.
Speed of execution is an obvious priority – but there are many other unique aspects of live streaming that complicate security strategies. These include:
- Variations in licensing policies, especially in cross-border distribution
- Requirements to reduce streaming latency in live viewing
- Vastly more streams to parse all at once in the search for illegal flows
- More illicit sources to identify and disrupt in near real time
Fortunately, these challenges can be overcome. This blog post outlines the requirements that must be met to mount an effective response.
Protecting live-streamed content from piracy
Multi-DRM support at ultra-low latency
Implementing a cloud-based next-generation security solution optimized for live streaming starts with a multi-DRM operations platform. Given the increased fragmentation of devices and rights policies, as well as the role of virtual multichannel video programming distributors (vMVPDs) as OTT service aggregators, such a platform must:
- Work seamlessly with the major proprietary DRM systems – Apple FairPlay Streaming, Google Widevine, Microsoft PlayReady, and Adobe Primetime – as well as with the open-standard Marlin DRM
- Protect and provision keys on both a per-session basis and throughout a viewing session, in accordance with the encryption methods and file formats each DRM supports to convey licenses and policy information
- Recognize whether a DRM license covers time-shifting use cases such as catch-up viewing, limited time windows, or cloud-based DVR options, and that the appropriate protections are provided
These strategies of protecting live-streamed content are best achieved through a uniform approach to content protection that marries the rights policies governing the vMVPD with the rights policies governing their OTT partners, eliminating the need for vMVPDs to re-encrypt content under a separate protection regime.
All the steps entailed in managing the execution of rights policies tied to a cloud-based multi-DRM service, whether under the control of an OTT provider or an vMVPD, pose a serious latency challenge. Consequently, the multi-DRM platform must ensure consistency in user experiences across all devices with the delay-free acquisition of keys from DRM servers, and prevent delays caused by license acquisition by end-users’ players in the initial authorization process.
Effective support for flagging stolen content
In battling piracy and protecting live-streamed content, a fast response is critical. Disruptions to pirated streams must occur before a live broadcast ends. Disruptions early in a game cause more pain to pirate audiences than later ones. A swift response must include detecting and following up on which streams are coming from unlicensed sources.
Many common approaches to identifying stolen streams of stored on-demand content – such as monitoring for branding labels or “hash codes” – are either too slow or have been made obsolete by pirate countermeasures.
A much more effective approach involves the use of web crawling tools in conjunction with digital fingerprinting technology, a mainstay in automatic content recognition (ACR) applications, to identify pirated content. Digital fingerprinting creates a digital signature from a few key video and audio descriptors that can uniquely identify if a piece of content is licensed to a specific distributor or licensee.
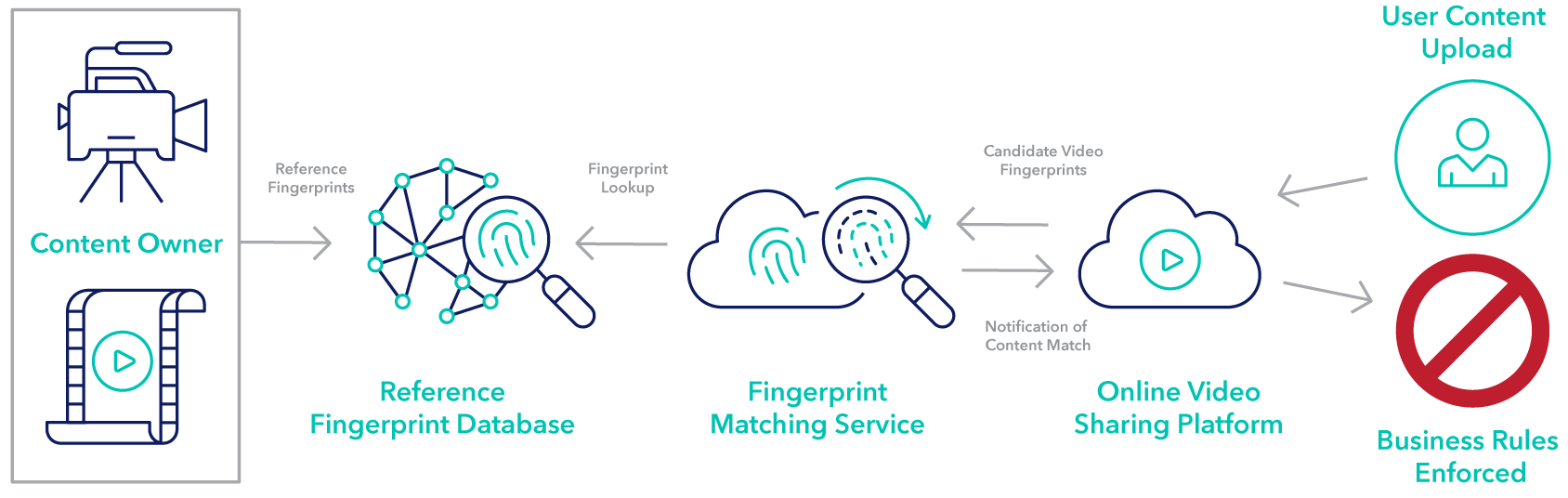
Forensic watermarking designed for live streaming
Though forensic watermarking was initially proposed in 2013 in MovieLabs’ Enhanced Content Protection (ECP) specifications, the scale of losses attributable to theft specially for live sports streaming has caused a strong push for forensic watermarking as a security requirement. This is certainly the case for sports streaming, and especially in the context of 4K UHD and HDR formatting becoming more commonplace.
To be effective at protecting live-streamed content, watermarking solutions must:
- Make it possible for license holders to disrupt viewing within a few minutes after streaming starts by detecting and decoding watermarks in read time
- Withstand pirate detection and the many means pirates have devised to render watermarks useless
- Survive content degradation in both the legitimate and piracy phases of distribution, including processes such as transcoding, recompression, and camcording
- Avoid adding noise or artifacts that could contribute to content degradation
- Work with persistently encrypted content, eliminating the need to decrypt and re-encrypt during content preparation and delivery
- Support extraction of the marks directly from the video for immediate identification of pirate sources, eliminating traditional “non-blind” approaches to detection that require comparison with the original unmarked video
- Be tightly integrated into a comprehensive security solution that orchestrates all aspects of protection to achieve the best possible results
Client-side vs. server-side watermarking
There are two basic approaches to forensic watermarking: one uses a server-side per-session injection of watermarks, while the other relies on client-side solutions securely integrated with media players or embedded in hardware that are sufficiently lightweight and versatile to work with any device.
For live streaming sports, the best results in any given moment can be attained by a market-validated client-side solution. The watermark extraction process can be performed in a minute or so compared to much longer identification processes (up to 15 minutes) in server-side applications. This is critical in order to stop live sports streaming piracy in real time.
In the case of linear streams delivering episodic programming that people will want to access later in on-demand mode, the server-side watermarking solution can be an option beside client side watermarking for protecting high-value linear streams formatted in 4K UHD and HDR. However, many server-side solutions rely on an “A/B” approach to marking, this can burden encoders, increase storage requirements, and consume more bandwidth – all adding additional complexity when integrating forensic watermarking solutions for live streaming services.
A well-designed comprehensive security platform supporting multi-DRM, live optimized forensic watermarking, and other requirements suited to protecting live-streamed content should provide distributors the option to meet the requirements set by rights holders and other considerations.
Other requirements impacting live content licensing
Beyond watermarking, there are other elements of MovieLabs’ ECP specifications that license holders include in their requirements for rights to stream live content. Even though these requirements were proposed in the motion picture context, they, like forensic watermarking, have moved into the broader realm of protection for multiple categories of content as piracy exacts an ever-higher toll on revenue.
For example, security mechanisms incorporated into any comprehensive content protection platform should also provide protection against app attacks where sources of pirated content substitute a phony ID for the real source’s ID.
Distributors must be sure the security platform they choose is equipped to meet ever broader stipulations, such as:
- Expanded hardware-level protection, using hardware roots of trust at the factory or through firmware reconfiguration
- Leveraging a secure video path (SVP) and Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) for separate protection-related processing
- Extending ECP protections beyond streaming to include content downloads, offline playbacks, device-to-device side loading, and time-shifting.
- Rigorous enforcement of device certification requirements through “trusted implementers” instead of relying on device OEMs to provide security compliance.
Producers and distributors of high-value sports and other live-streamed content now have the opportunity to combat piracy effectively. To learn more about protecting live-streamed content, read the full whitepaper.








